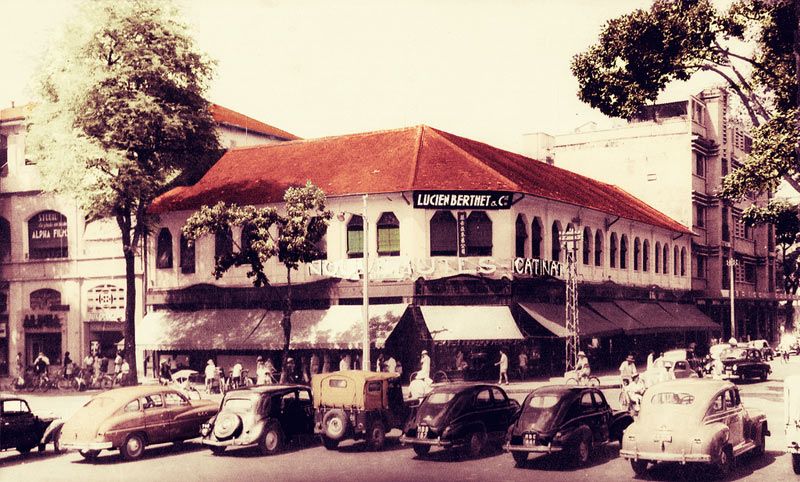Housed in one of the city’s most outstanding modernist buildings, the former South Vietnamese National Library was the culmination of over 100 years of library development in the southern metropolis.
The origins of the Hồ Chí Minh City General Sciences Library may be traced back to the Documentation Library of the Government of Cochinchina (Bibliothèque de Documentation du Gouvernement de la Cochinchine Française), which was set up by Admiral-Governor Marie Gustave Hector Ohier in 1868.
In 1882 it was transformed into a public library named the Library of Saigon (Bibliotheque de Saigon). Following the construction of the Government Secretariat compound at 27 rue de Lagrandière (now 159-161 Lý Tự Trọng) in 1888, it was found a new home on the upper floor of that building.

The Government Secretariat compound at 27 rue de Lagrandière (now 159-161 Lý Tự Trọng) where the library was once housed.
In 1902, the library was renamed the Library of Cochinchina (Bibliotheque de la Cochinchine), and by 1909 it is said to have amassed a sizeable collection of over 10,000 volumes on law, sciences, history and literature, along with newspapers and journals.
In 1917, the Directorate of Archives and Libraries (Directorate des archives et bibliothèques) was set up by the colonial government under the management of Paul Boudet (1888-1948), to oversee the development of archives and libraries in Indochina, and the Library of Cochinchina became a branch of the Directorate, under the management of Saigon librarian, Saint-Marty.
Soon after 1920, the Library of Cochinchina moved to larger premises just across the road at 34 rue de Lagrandière, right next door to the Gendarmerie. Nonetheless, as it still had to share accommodation with the Archives, space remained extremely limited. On 2 November 1924, the newspaper L'Eveil économique de l'Indochine commented: “The current building, despite the significant changes that have been made, does not meet the developmental needs of the library; it is too small for a real, modern library, and therefore, consideration is being given to moving the library into a larger and more appropriate building, while the Archives, already quite conveniently placed in front of the government offices, will remain in the current location.”

34 rue de Lagrandière/Gia Long (now Lý Tự Trọng) street, where the library was based from the 1920s until 1971.

34 rue de Lagrandière/Gia Long (now Lý Tự Trọng) street today.
In fact, it would be another 50 years before this move to a larger building could take place, although a temporary solution was found in 1926 by opening a separate lending library at 160 rue Catinat (Đồng Khởi street). In 1927, a small children's library was also set up within the main library building. By 1931, the Library of Cochinchina had a total stock of over 30,000 volumes.
Related Articles:
- Old Saigon Building Of The Week: The Former Cercle Sportif Saïgonnais
- Old Saigon Building Of The Week: The Second Chambre de Commerce Building
- Old Saigon Building Of The Week: The Former Lycée Chasseloup-Laubat
In 1949, the Library of Cochinchina was transferred to the Service of Education of the newly-established State of Việt Nam and renamed the Library of the South (Thư viện Nam phần). At this time, a separate Children's Reading and Lending Library (Thư viện cho Mượn và phòng Ðọc thiếu nhi) was opened at 194D Pasteur. A 1950 report to UNESCO described the Library of the South as “a general library of nearly 70,000 volumes and a copyright deposit library for all materials published in the South.”
The collection was augmented further in 1956, when the General Library of the Lycée Pétrus Ký – at that time run by the University of Saigon – received over 25,000 items which had been transferred in the previous year from Hà Nội, and was placed under the control of the Library of the South.
In January 1957, the Library of the South’s three campuses – the former Library of Cochinchina, the Lycée Pétrus Ký General Library and the Children's Reading and Lending Library – were joined with the Ðà Lạt Library to become the National Library of the Republic of Việt Nam, under the direct administration of the RVN Ministry of National Education. Two years later, a Directorate of Archives and Libraries was set up within the Ministry. By this time, the holdings of the National Library comprised in excess of 85,000 volumes, most of them French.
In 1953, a new prison was opened in Chí Hòa (now District 10) to replace the overcrowded Maison Centrale de Saigon, which then occupied most of the block encircled by Gia Long (Lý Tự Trọng), Công Lý (Nam Kỳ Khởi Nghĩa), Lê Thánh Tôn and Nguyễn Trung Trực streets. Two years later, President Ngô Đình Diệm drew up plans to build a grand new National Library building on the old prison site. However, because of the prevailing political and economic situation, the project quickly ground to a halt. Consequently, the existing three-campus library continued in operation and the old Maison centrale building survived as a temporary detention facility for a further decade.

The National Library was built on the site of the former Maison centrale.
During the 1960s and early 1970s, the National Library received significant funding and assistance from USAID’s Library Development Activity (LDA) programme, which enabled it to expand its collection and develop its human resources.
In 1968, the Maison centrale was demolished and construction of the new National Library finally got under way, funded by a special national lottery. Built to a striking and innovative design by local architects Nguyễn Hữu Thiện, Bùi Quang Han and Huỳnh Tấn Phát, the new building is said to have cost more than 130 million piastres. It was inaugurated on 23 December 1971 at a ceremony presided over by South Vietnamese President Nguyễn Văn Thiệu.
After Reunification, the former South Vietnamese National Library was integrated into the national library system of the Socialist Republic of Việt Nam. In 1976 it was renamed the National Library II (Thư viện Quốc gia II, Thành Phố Hồ Chí Minh), but two years later it became the Hồ Chí Minh City General Sciences Library (Thư viện Khoa học Tổng hợp, Thành Phố Hồ Chí Minh), the name by which it is known today.
After the opening of the new National Library in 1971, the old Library of Cochinchina building at 34 Gia Long (Lý Tự Trọng) became the Library of the Saigon Archaeology Institute (Viện Khảo cổ Sài Gòn). The building was extensively remodelled after 1975 and has since served as the Library of the Institute of Social Sciences, Southern Region.

A First Day Cover of 1974 featuring the National Library building.
During the latter years of colonial rule, many Vietnamese revolutionaries had been detained in the former Maison centrale and several were tortured and executed there. After 1975, the road in front of the Hồ Chí Minh City General Sciences Library was renamed Lý Tự Trọng street, in honour of one of the Maison centrale’s most famous victims, whose bust also stands in the garden at the front of the library. Here visitors will also find, prominently displayed, a plaque which recalls in Vietnamese some of the momentous events in the revolutionary struggle which took place in the prison.

Tim Doling is the author of the walking tours book Exploring Hồ Chí Minh City (Nhà Xuất Bản Thế Giới, Hà Nội, 2014) and also conducts 4-hour Heritage Tours of Historic Saigon and Cholon. For more information about Saigon history and Tim's tours visit his website, www.historicvietnam.com.